Chap 10. Cellular Wireless networks
< 4G/5G cellular networks >
- 움직이면서 끊김없이 통신하고 싶음 → wide-area mobile Internet의 해결방안
- widespread deployment/use (배치/사용)
: mobile-broadband-connected devices > fixed-broadband-connected devices devices (5:1 in 2019)
: 4G availability: 97% of time in Korea (90% in US)
- 최대 transmission rates: 100’s Mbps
- technical standards: 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
: wwww.3gpp.org
: 4G: Long-Term Evolution (LTE) standard
> cellular networks가 wired Internet과 비슷한 점
- edge/core에서만 다르고, 둘 다 same carrier 아래 있다.
- global cellular network: a network of networks
- widespread use of protocols we’ve studied
: HTTP, DNS, TCP, UDP, IP, NAT, separation of data/control planes, SDN, Ethernet, tunneling
- wired Internet에 상호연결
> cellular networks와 wired Internet의 차이점
- different wireless link layer
- mobility
- user “identity” (via SIM card)
- business model
: 사용자가 cellular provider에 가입
: 뚜렷한 “home network” versus roaming on visited nets
: global access, with authentication infrastructure, and inter-carrier settlements
< Elements of 4G LTE architecture >
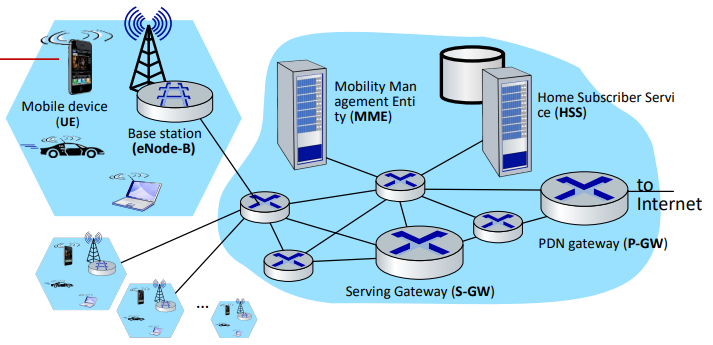

1. Radio access network의 구성요소
> Mobile device (Use Equipment - UE)
- smartphone, tablet, laptop, IoT, with 4G LTE radio
- International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
: SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card에 저장된 64-bit 기기 고유의 식별번호
: 잃어버렸을 때 도난 신고 가능
> Base station (eNode-B)
- at “edge” of carrier’s network(EPC)
- wireless radio resources, mobile devices in its coverage area(cell) 를 관리
- device authentication을 다른 요소와 coordinate
- WiFi AP와 비슷하지만 다음과 같은 차이가 존재
→ 사용자의 mobility에 대해 active role
→ radio 사용을 최적화하기 위해 근처의 base stations와 협력하는 것이 중요 (radio가 겹치지 않도록)
2. EPC의 구성요소
> Home Subscriber Service (HSS) - 컨트롤
- HSS’s network가 “home network”인 모바일 장치에 대한 기본적인 정보 저장
- works with MME in device authentication
> Mobility Management Entity (MME) - 컨트롤
- device authentication (device-to-network, network-to-device) coordinated with mobile home network HSS
- path (tunneling) setup from mobile device to P-GW
: 가상의 패스(IP tunnel)를 만들어서 P-GW로 데이터를 전송
- mobile device management
: device handover between cells
: tracking/paging device location
> Serving Gateway (S-GW), PDN Gateway (P-GW) - 데이터
- lie on data path from mobile to/from Internet
- other routers: tunneling의 광범위한 사용
*P-GW (PDN Gateway) - 데이터
: mobile cellular network로의 출입문
: 다른 internet gateway router와 유사
: NAT 서비스 제공
< LTE: data plane control plane separation >
| control plane | data plane |
 |
 |
- mobility management, security, authentication을 위한 new protocol |
- link, physical layers에서의 new protocol - 이동성을 촉진하기 위한 tunneling의 광범위한 사용 |
< LTE data plane protocol stack: first hop >
> LTE link layer protocols
- Packet Data Convergence(통합)
: header compression, encryption (암호화)
- Radio Link Control (RLC) Protocol
: fragmentation /reassembly, reliable data transfer
- Medium Access
: requesting, use of radio transmission slots

> LTE radio access network

- downstream: FDM, TDM within frequency channel
(OFDM - orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)
- “orthogonal”- channels간의 간섭 최소화
- upstream: FDM, TDM similar to OFDM
- 각 active mobile 기기는 2개 이상의 0.5ms time slots을 할당 over 12 frequencies
- scheduling algorithm의 표준화 x (operator까지)
- 기기당 100’s Mbps 가능
*다운속도>>업속도
< LTE data plane protocol stack: packet core >
- tunneling
: 가상의 layer를 만들어 쉽게 base station과 end 지점만 고려하여 routing 되도록 함
: mobile datagram encapsulated using GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP), sent inside UDP datagram to S-GW
: S-GW re-tunnels datagrams to P-GW
: supporting mobility - mobile 사용자가 움직일 때, tunneling endpoints만 변화

< BS(Base Station)와의 연결 과정 >

1. BS는 모든 주파수에 primary synch signal(beacon)를 5ms마다 broadcasts
- BSs from multiple carriers may be broadcasting synch signals
2. mobile은 primary synch signal를 찾고 이 주파수에서 2nd synch signal을 찾는다.
- BS에 의해 broadcast 된 정보를 찾는다 (channel bandwidth, configurations, BS’s cellular carrier info)
- multiple base stations, multiple cellular networks으로부터 정보를 얻는다.
3. mobile이 연결할 BS 선택
예) preference for home carrier(kt, skt 등) - 로밍을 하면 해외에서도 가능
4. authenticate, establish state, set up data plane 등의 단계가 더 필요
< LTE mobiles: sleep modes >

LTE mobile은 배터리 절약을 위해 radio를 “sleep”상태로 둔다. (as in WiFi, Bluetooth)
- light sleep
: after 100 msec of inactivity
: downstream 전송을 확인하기 위해 주기적으로 wake up (100 msec)
- deep sleep
: after 5-10 secs of inactivity
: deep sleeping동안 mobile이 cells을 변경시킬 수 있다.
연결을 끊는다 → need to re-establish association
< Global cellular network: a network of IP networks >

- home network HSS
: identify & services info (in home network, roaming)
- all IP (Visited network)
: carriers interconnect with each other,
and public internet at exchange points
: legacy 2G, 3G: not all IP, handled otherwise
< On to 5G! >
- 목표
: peak bitrate 10배↑, latency 10배↓, traffic capacity over 4G 100배↑
- 5G NR (new radio)
: two frequency bands - FR1 (450 MHz–6 GHz) / FR2 (24 GHz–52 GHz): millimeter wave frequencies
: not backwards-compatible(역호환) with 4G
: MIMO - multiple directional antennae
- millimeter wave frequencies (고주파)
: data 속도↑, distances↓
: pico-cells: cells diameters: 10-100 m (WiFi 수준)
: massive, dense한 새로운 base stations가 필요
교재는 Data and Computer Communications를 참고하였고, 자료는 이화여자대학교 이형준 교수님의 정보통신공학 강의에서 가져온 것입니다.
'Study > 정보통신공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Week 12-2] LAN - Addressing, ARP, Topology (0) | 2023.05.24 |
|---|---|
| [Week 12-1, 12-2] Cellular networks - Mobility (0) | 2023.05.22 |
| [Week 11-1] WiFi: 802.11 wireless LAN (0) | 2023.05.10 |
| [Week 10-1, 10-2] Cellular Wireless networks (0) | 2023.05.06 |
| [Week 9-2] WAN (Wide Area Networks) (0) | 2023.05.02 |