Chap 7. Data Link and Control Protocols
< Data Link Control Protocols >
: directly connected, wire-like
: Losses, and errors
: no out-of-sequence frames
: 적용 - direct links, LANS, Connections across WANs
예) PPP, HDLC, Ethernet LAN, IEEE 802.11(Wifi) LAN

> Services
- Framing (Frame synchronization)
- Flow control
- Error control
- Addressing
- Control and data
- Link Maintenance
- Multiplexing
- Security: Authentication & Encryption
< Framing >
: Mapping stream of physical layer bits into frames
: Mapping frames into bit stream
: frame을 나눌 때 사용되는 방식
- Character Counts, Control Characters, Flags, CRC Checks
< Flow Control >
: transmitting entity가 receiving entity의 data를 over-whelm하지 않도록 보장하는 기술
– The receiving entity는 전송을 위해 maximum data buffer를 할당
– data가 수신되면, receiver 데이터를 higher-level software에 전달하기 전에 일정량의 처리를 수행
: Flow Control이 없다면 오래된 데이터를 처리하는 동안 receiver의 buffer가 차 overflow 발생
> Stop-and-wait flow control
> Sliding-window flow control
< Stop-and-Wait Flow Control >
: Simple form of flow control
: 하나 보내고 대기 후 ACK 수신
Source가 frame을 전송
→ Destination은 frame을 받고 acknowledgement(ACK)를 Source에 전송
→ Source는 ACK를 받기 전까지 next frame을 전송 x
→ Destination이 꽉차면 ACK를 보내지 않음으로 flow를 조절
: source가 큰 데이터 블록을 더 작은 블록으로 나누고 많은 프레임으로 데이터를 전송
– receiver의 buffer 크기가 제한
– 전송 시간 ↑→ 오류 발생 가능성↑ → 전체 프레임 재전송
– shared medium에서는 일반적으로 한 station을 장시간 허용하지 않는 것이 바람직
→ 따라서 다른 sending station에서 긴 delay 발생

< Sliding Windows Flow Control >
: multiple numbered frames를 전송
: Receiver에 W(window: 동시에 보낼 수 있는 사이즈) 길이의 buffer 존재
: Transmitter는 ACK없이 최대 W frames 전송 → 모두 전송 후 ACK전송
: ACK에 예상되는 다음 frames 포함
예) RR3 → 3을 받을 준비 o → 0, 1, 2 받음
: Sequence number는 field 크기(k)로 제한
→ Frames are numbered modulo 2^k
→ Giving max window 최대 2^k – 1: 0 < W <= 2^k - 1
: Receiver가 추가 전송의 허용 없이 frame ACK 가능 (Receive Not Ready(RNR) - 더 이상 보내지마)
: 다시 시작하려면 일반 승인을 전송
: If have full-duplex link, can piggyback ACKs
예) A → B 데이터 전송 / B → A ACK전송 / B → A 데이터 전송 / B → A ACK전송...
자원 낭비! → piggyback 사용 (ACK를 실어 데이터와 함께 전송)
*half-duplex: A → B로 보내기만 함, full-duplex: A ↔ B 모두 주고 받음


frame = window = 7, k = 3 → 7 = 2^3 - 1
1. sender는 0 ~ 6까지 전송 가능
2. 데이터 0, 1, 2를 전송하고 아직 3, 4, 5, 6은 전송 x
3. window 감소
4. 데이터 0, 1, 2에 대한 ACK수신(RR3) 후 ACK된 프레임만큼 윈도우 이동
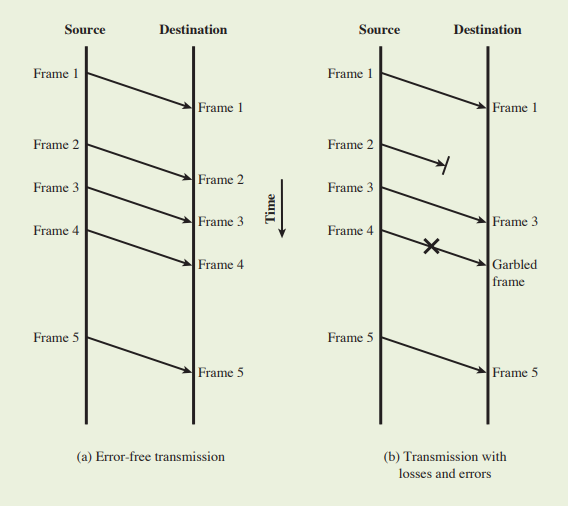
< Error Control Techniques >
- Error detection → ACK를 다시 보냄
- Retransmission after timeout
- Positive acknowledgment - 잘 받은 것에 대한 ACK
- Negative acknowledgment and retransmission - 오버헤드가 클 때는 못 받은 것에 대한 ACK
예) 1~10 중 3만 못 받았을 때
- Lost frames: frame이 다른 쪽에 도착하는 데 실패
- Damaged frames: frame은 도착했지만 몇몇 bits에 오류 발생
- Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ)
< Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) >
: 근거리, 불안정, 저전력, 효율적으로 가끔 통신, S/N이 약함
: 빠르게 전달하기 보다는 재전송이 목표
: Collective name for error control mechanisms
: unreliable data link를 reliable하게 변경해 준다
> Stop-and-wait ARQ
> Go-back-N ARQ
> Selective-reject ARQ

< Stop-and-wait ARQ >
1. Source가 single frame을 전송 (TX)
2. Receiver는 ACK 대기 (RX)
: destination의 reply가 도착하기 전까지는 어떤 데이터도 전송 x
3. If frame received is damaged, discard it
: Transmitter has timeout
: If no ACK within timeout, retransmit
4. If ACK is damaged, transmitter는 알 수 x
: Transmitter will retransmit
: ACK가 보내지지 않으면 sender는 frame 재전송
: Receiver는 똑같은 frame을 2개 받는다
: Use alternate numbering and ACK0 / ACK1
< Go-Back-N ARQ >
: 가장 많이 사용되는 error control
: Based on sliding-window
: outstanding frames의 수를 control하기 위해 window size 이용
> 오류x → the destination will acknowledge incoming frames as usual
– RR = receive ready, or piggybacked acknowledgment
> destination station이 frame에서 오류를 발견 → negative acknowledgment 전송
– REJ = reject
– Destination will discard that frame and all future frames until the frame in error is received correctly
– Transmitter must go back and retransmit that frame and all subsequent frames
< Selective-Reject ARQ >
: "selective retransmission"
: rejected frames만 재전송
: Subsequent frames are accepted by the receiver and buffered
: Minimizes retransmission
: Receiver large enough buffer를 준비해야 한다
: More complex logic in transmitter – Less widely used
: Useful for satellite links with long propagation delays

< Error Control in Data link layer >
: Data link operates over wire-link, directly-connected systems
: 프레임은 corrupted, lost 될 수 있지만 순서대로 도착
: data link는 error chaecking, retransmission을 수행
: 두 시스템 간의 error-free packet transfer
// 중간 시험범위 - 여기까지 //
< High Level Data Link Control (HDLC) >
> normal response mode (NRM)
> Asynchronous Balanced Mode (ABM)
> Asynchronous Response Mode (ARM)
< normal response mode (NRM) >
: Primary initiates transfer
: polling multidrop lines 사용
: unbalanced configuration 사용
< Asynchronous Balanced Mode (ABM) >
: full-duplex point-to-point links 사용
: balanced configuration 사용
: Either station initiates transmission
: Has no polling overhead
: 가장 많이 사용
< Asynchronous Response Mode (ARM) >
: unbalanced configuration 사용
: Secondary may transmit without permission from primary
: 거의 사용 x
교재는 Data and Computer Communications를 참고하였고, 자료는 이화여자대학교 이형준 교수님의 정보통신공학 강의에서 가져온 것입니다.
'Study > 정보통신공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Week 9-2] WAN (Wide Area Networks) (0) | 2023.05.02 |
|---|---|
| [Week 9-1] High Level Data Link Control (HDLC) (0) | 2023.04.28 |
| [Week 6-1, 6-2] Error Detection and Correction (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| [Week 5-2] Data encoding (Digital Data → Analog Signal, Analog Data → Digital Signal) (1) | 2023.04.13 |
| [Week 5-1] Data Encoding (Digital data → Digital signal) (0) | 2023.04.13 |