Chap 5. Data Encoding
< Digital Data → Analog Signal >
: public telephone system
: analog signals를 receive, switch, transmit 하도록 설계
: 주파수 범위 - 300Hz ~ 3400Hz
: subscriber locations의 digital signals를 처리하는 데 적합 x
: modem(modulator-demodulator)을 사용하여 digital data -> analog signal / analog signal -> digital data
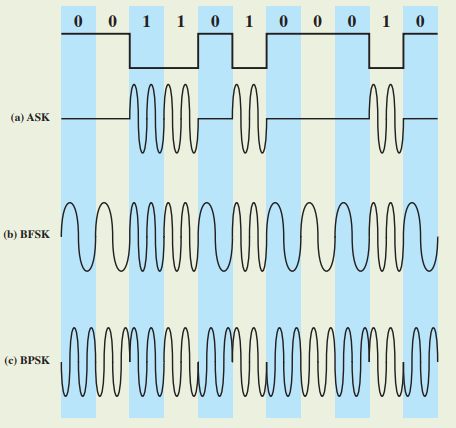

< Definition of Analog Signal Encoding Formats >
1) ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)
0 - 중간 (no line signal)
1 - sine 2번
2) BFSK (Binary Frequency Shift Keying) - FSK
0 - sine 1번
1 - sine 2번
3) BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) - PSK
0 - sine 2번 아래 -> 위
1 - sine 2번 위 -> 아래
4) DPSK (Differential Phase Shift Keying) - PSK
0 - 이전과 모양이 동일한 sine 2번
1 - 이전과 모양이 다른 sine 2번
5) MFSK (Multiple FSK) - FSK

M = 4일 때,
11 - fc + 3fd
10 - fc + fd
01 - fc - fd
00 - fc - 3fd
< ASK >
: Encode 0/1 by different carrier amplitudes
: Usually have one amplitude 0
: 갑작스러운 gain changes에 취약
: Inefficient
: Up to 1200bps on voice grade lines
: optical fiber (광섬유)를 통한 빠른 속도
< BFSK >
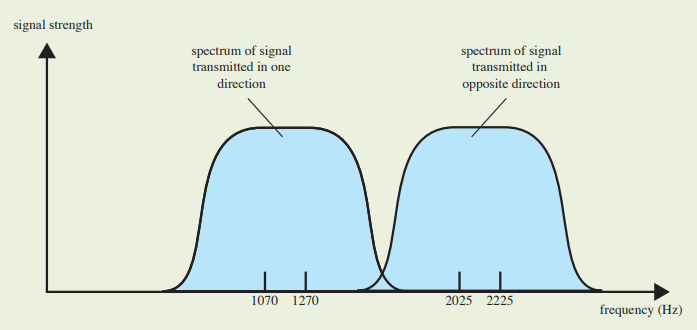
: FSK의 가장 일반적인 형태
: Two binary values는 two different frequencies
(near carrier) 로 표시
: ASK보다 오류에 덜 취약
: Up to 1200bps on voice grade lines
: High frequency radio (고주파 라디오)
: coaxial cable을 사용하는 LANs보다 주파수 ↑
< Phase Shift Keying (PSK) >
: The phase of the carrier signal이 데이터를 나타내기 위해 이통
> Binary PSK (BPSK)
: Two phases represent the two binary digits
> Differential PSK (DPSK)
: Phase shifted relative to previous transmission rather than some reference signal
< Multiple FSK (MFSK) >
: Each signaling element represents more than one bit
: 2개이상의 frequencies 사용
: More bandwidth efficient
: 오류에 더 취약

< Bandwidth & BER(Bit error) >
| ASK | MFSK | MPSK |
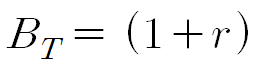 |
 |
 |
| M ↑ → bandwidth ↑, BER ↓ | M ↑ → bandwidth ↓, BER ↑ |

< Performance of Digital to Analog Modulation Schemes >
> Bandwidth
: ASK/PSK - bandwidth directly relates to bit rate
: Multilevel PSK - gives significant improvements (개선사항)
> In presence of noise
: PSK, QPSK의 bit 오류율 = ASK, FSK보다 3dB 우수
: MFSK, MPSK는 bandwidth efficiency와 error performance 간에 tradeoff를 가진다
< Analog Data → Digital Signal >
Digitization
: analog data → digital data로의 전환
: NRZ-L 사용
: NRZ-L이 아닌 다른 코드 사용
: Be converted to analog signal
A2D : codec 사용
- Pulse code modulation (PCM)
- delta modulation

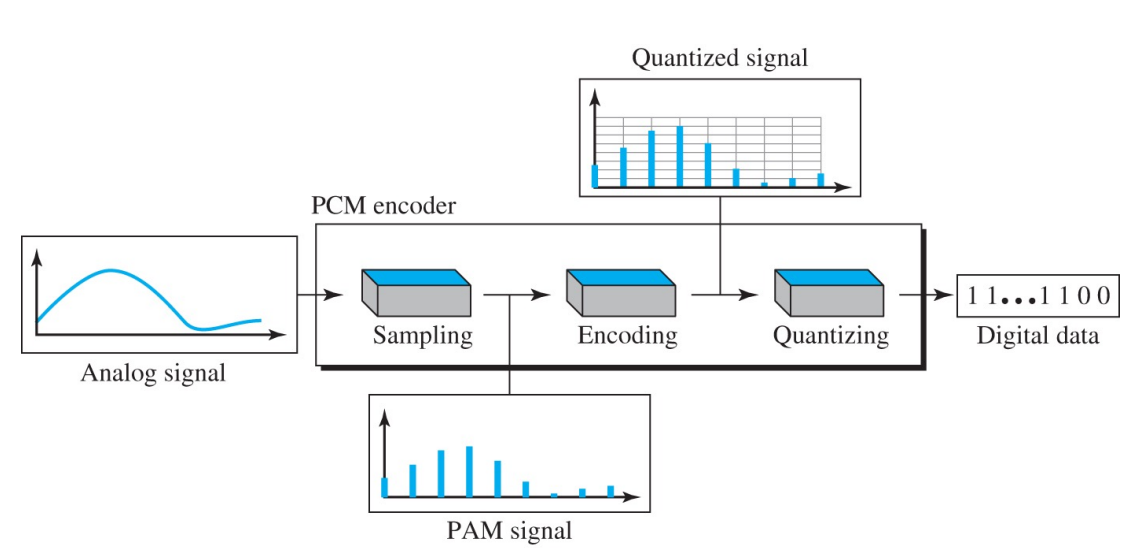
< PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) >
: PAM된 아날로그 신호를 Sampling/Encoding/Quantizing 과정을 거쳐 디지털 신호를 생성
* PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation)
- Analog samples
- digital로 전환하기 위해, 각각의 analog samples은 binary code로 할당되어야 한다
: Sampling → Quantization → Encoding → Decoding → Filterling
: PAM sampler → Quantizer → Encoder

: Sampling Theorem에 기초
"신호 f(t)가 일정한 시간 간격으로 샘플링되고 최고 신호 주파수의 두 배 이상의 속도로 샘플링되면,
샘플에는 원래 신호의 모든 정보가 포함됩니다.
f(t)는 lowpass filter를 사용하여 이러한 샘플로부터 재구성할 수 있습니다."

< Non-Linear Coding >

교재는 Data and Computer Communications를 참고하였고, 자료는 이화여자대학교 이형준 교수님의 정보통신공학 강의에서 가져온 것입니다.
'Study > 정보통신공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Week 7-1, 7-2] Data Link Control Protocols (0) | 2023.04.14 |
|---|---|
| [Week 6-1, 6-2] Error Detection and Correction (1) | 2023.04.13 |
| [Week 5-1] Data Encoding (Digital data → Digital signal) (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| [Week 4-2] Transmission Media - Wire, Wireless (1) | 2023.04.12 |
| [Week 4-1] Data Transmission (2) | 2023.04.12 |