Chap 2. Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Application
< Creating a Network App >
: end system에서만 동작 o
: network을 통해 communication
: network-core device에서 동작 x (router는 IP주소만 확인)

< Client-Server Paradigm >
- Server
: 항상 켜져 있어야 한다 (always-on)
: 고정적으로 1개의 IP주소만 가져야 한다 (permanent IP address)
: 가끔 data center로 존재하기도 한다.
- Client
: 연결/접속 여부가 달라진다 (intermittently connected)
: 항상 Server와 통신
: have dynamic IP address - 네트워크 연결할 때 마다 달라진다
: do not communicate directly with each other
예) HTTP, IMAP, FTP

< Peer-peer Architecture >
- Server
: 항상 켜져 있지 않다 (no always-on)
: change IP address → 복잡
: data center 구축 x
: end system끼리 directly communicate
: peer는 서비스를 요청 & 제공 → 한 host내에 client & server 동시 존재
예) P2P file sharing
*self scalability: 새로운 peer가 나타나도 서비스를 확장시킬 필요 x
< Process communicating >
*process
: host안에서 작동하는 프로그램
*Client process: 통신을 시작하는 프로세스
*Server process: 연결을 기다리는 프로세스
> Within 같은 host (1개의 host)
: 2개의 process는 OS에 의해 IPC(Inter-Process Communication)을 한다
*IPC: 프로세스 간의 데이터 교환(한 기기 내에서)
> Within 다른 host
: exchanging messages에 의해 다른 기기와 통신한다
< Sockets >
: application layer(개발자 통제), transport layer(OS통제)의 통과문
: end system마다 부착
: 프로세스는 socket을 통해 메시지를 주고 받는다

< Addressing process - IP주소 + Port # >
: 메세지를 받기 위해서 프로세스는 identifier(식별자)를 가져야 한다
: host device - unique 32bit IP address
: IP 주소 만으로는 한 host내에서 실행되는 process를 식별 x → 또 다른 식별자 필요 → Port number
예) HTTP: 80, mail server: 25
예) web server로 보내는 HTTP message의 식별자 - IP주소: 128.119.245.12, Port #: 80
< Application-layer protocol이 정의하는 것 >
- 메세지의 종류: request, reponse
- 메세지의 syntax(문법): 어떤 field가 존재하는 지, 어떻게 구분할 지
- 메세지의 semantics(의미)
- rules: 메세지를 언제, 어떻게 보내고 받을 지
*open protocol
: RFCs(Request for Comments)로 정의 → 누구나 프로토콜 definition에 접근 가능
*RFCs: 국제 인터넷 표준화 기구에서 관리 / "RFC-일련번호"
: interoperability(상호 운용성) 제공 → HTTP(web기반), SMTP(메일 전송)
*proprietary protocols(독점 프로토콜: 개인이나 조직이 마음대로 만든 규정) → skype, zoom
< 앱에 필요한 transport service >
1) data integrity (데이터 온전성, 유실 x)
: file transfer, web transfer - 100%의 데이터 전송 신뢰성을 요구
: audio, video - tolerate some loss
2) timing
: internet telephony, interactive games - 낮은 delay를 요구
3) throughput (처리량)
: multimedia - 최소한의 처리량을 요구
: elastic apps (email, FTP, web transfer) - 모든 throughput 사용
4) security
: encryption(암호화), data integrity(데이터 무결성)
: http - secure x / https - secure o

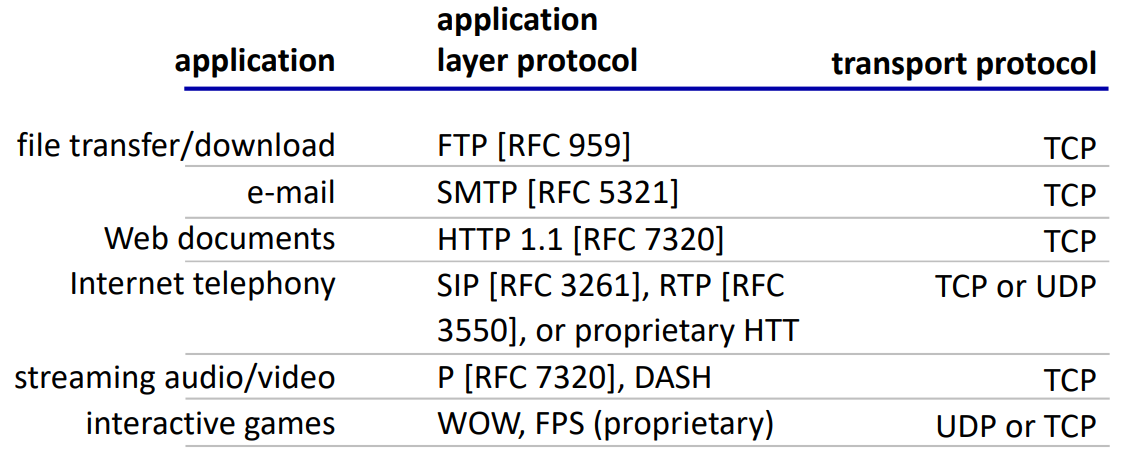
- SIP - call setup → TCP 적합
- RTP - 오디오 → UDP 적합
< Vanilla TCP & UDP sockets >
* vanilla - 아무 것도 안한 상태
: encryption(암호화) x
: 소켓으로 전송된 cleartext passwords는 cleartext로 인터넷을 통과
< TLS(Transport Layer Security) >
: 암호화된 TCP 연결 제공 (encryption)
: data integrity (데이터 무결성)
: end-point 인증
: 앱 → TLS 라이브러리 사용 / TLS 라이브러리 → TCP 사용
: TLS socket API - 소켓으로 전송된 cleartext → 암호화된 인터넷 (Ch.8)
교재는 Data and Computer Communications를 참고하였고, 자료는 이화여자대학교 이형준 교수님의 정보통신공학 강의에서 가져온 것입니다.
'Study > 정보통신공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Week 3-2] Socket programming for TCP and UDP (0) | 2023.04.11 |
|---|---|
| [Week 3-1] Web - HTTP, Cookie, Cache, E-mail (0) | 2023.04.10 |
| [Week 2-2] Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP (0) | 2023.04.09 |
| [Week 2-1] Network Core - Packet/Circuit switching, Internet structure (0) | 2023.04.08 |
| [Week 1-2] The Internet and Network Structure (0) | 2023.04.08 |